- algebra. The substitution of symbols and letters for numerical variables and constants. These symbols can be manipulated in the same way as numbers and form the basis for most mathematical calculations.
- abscissa. The x-coordinate of a point in a 2-dimensional coordinate system.
- absolute value. The positive value for a real number, disregarding the sign. Written |x|. For example, |3|=3, |-4|=4, and |0|=0.
- algebraic equation. An equation of the form f(x)=0 where f is a polynomial.
- algebraic number. A number that is the root of an algebraic polynomial. For example, sqrt(2) is an algebraic number because it is a solution of the equation x2 = 2.
- angles. The inclination of one line to another. Angles are measured in degrees or radians. One revolution of a circle = 360° = 2pi radians.
- annulus. The region enclosed by two concentric circles.
- arithmetic. The manipulation of numbers by addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and extraction of roots.
- arithmetic mean. The arithmetic mean of n numbers is the sum of the numbers divided by n.
- average. Typically this refers to the arithmetic mean.
- base. The number of single digit numerals in a counting system. The decimal system has base 10 (0,1,2,...,9) and the binary system base 2 (0 and 1). In the expression xy, x is called the base and y is the exponent.
- binary number. A number written to base 2.
- binary operation. A binary operation is an operation that involves two operands. For example, addition and subtraction are binary operations.
- binomial. An expression that is the sum of two terms such as a + b or a - b.
- binomial coefficient. The coefficients of x in the expansion of (x+1)n.
- bisect. To cut in half.
- calculus. The study of continuous change in functions. The two branches of calculus are differentiation and integration. Differentiation is the determination of the rate of change in a function. Integration is the summation of the changes in a function, normally regarded as the area under a curve.
- catenary. A curve whose equation is y = (a/2)(e x/a + e -x/a). A chain suspended from two points forms this curve.
- central angle. An angle between two radii of a circle.
- chord. The line joining two points on a curve is called a chord.
- circle. The set of points equidistant from a given point (the center). A circle is the path proscribed by point that rotates about a fixed origin.

- circular cone. A cone whose base is a circle.
- circumcenter. The circumcenter of a triangle is the center of the circumscribed circle.
- circumcircle. The circle circumscribed about a figure.
- coefficient. The number part of an algebaric term: in 4x², 4 is the coefficient.
- complementary angles. Two angles whose sum is 90o.
- complex number. The sum of a real number and an imaginary number, for example 3+4i where i=sqrt(-1).
- concave. Curved from the inside.
- congruent figures. two geometric figures that are identical in size and shape.
- conic section. The cross section of a right circular cone cut by a plane. An ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola are conic sections.
- coordinate geometry. System of geometry where points, lines, shape and surfaces are represented by algebraic expressions. These expressions can be presented as graphical solutions (graphs) in two of three dimensions.
- cubic equation. A polynomial equation of degree 3.
- decimal number. A number written to the base 10.
- deficient number. A positive integer that is larger than the sum of its proper divisors.
- degree. The degree of a term in one variable is the exponent of that variable. For example, the degree of 7x5; is 2.
- denominator. In the fraction x/y, x is called the numerator and y is called the denominator.
- diagonal. In a polygon, the line segment joining a vertex with another (non-adjacent) vertex is called a diagonal.
- diameter. The longest chord of a figure. In a circle, a diameter is a chord that passes through the center of the circle.
- differential calculus. That part of calculus that deals with the opeation of differentiation of functions.
- digit. In the decimal system, one of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
- dihedral angle. The angle formed by two planes meeting in space.
- dividend. In the expression "a divided by b", a is the divident and b is the divisor.
- divisor. In the expression "a divided by b", a is the divident and b is the divisor.
- dodecaedron . A solid having 12 plane faces.
- domain. The domain of a function f(x) is the set of x values for which the function is defined.
- duodecimal number system. The system of numeration with base 12.
- elementary function. one of the functions: rational functions, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions.
- ellipse . A closed plane curve generated by a point moving in such a way that the sums of its distances from two fixed points is a constant: a plane section of a right circular cone that is a closed curve. A plane figure whose equation is: x2/a2+y2/b2=1.
- ellipsoid. A solid figure whose equation is x2/a2+y2/b2+z2/c2=1.
- equation. A set of mathematical symbols split by an equals sign (=). Terms are symbols that are added or subtracted. Factors are symbols that are multiplied or divided.
- equilateral polygon. A polygon all of whose sides are equal.
- equilateral triangle. A triangle with three equal sides.
- even number. An integer that is divisible by 2.
- exponent. In the expression xy, x is called the base and y is called the exponent. See also index.
- exponential function. The function f(x)=ex.
- expoential function to base a. The function f(x)=ax.
- factor. The integer divisors of a number. 1, 2 and 7 are the factors of 14.
- factorial. n! (read n factorial) is equal to the product of the integers from 1 to n.
- Fermat number. A number of the form 2(2n)+1.
- Fibonacci number. A member of the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5,... where each number is the sum of the previous two numbers.
- formula. A concise statement expressing the symbolic relationship between two or more quantities.
- fraction. An expression of the form a/b.
- frequency. The number of times a value occurs in some time interval.
- frustum. For a given solid figure, a related figure formed by two parallel planes meeting the given solid. In particular, for a cone or pyramid, a frustum is determined by the plane of the base and a plane parallel to the base. NOTE: this word is frequently incorrectly misspelled as frustrum.
- Gaussian curve. A normal curve.
- geometry. The study of two and three dimensional space.
- geometric progression. A sequence in which the ratio of each term to the preceding term is a given constant.
- geometry. The branch of mathematics that deals with the nature of space and the size, shape, and other properties of figures as well as the transformations that preserve these properties.
- golden ratio. (1+Sqrt[5])/2.
- graph. A graph is a set of points (called vertices) and a set of lines (called edges) joinging these vertices.
- great circle. A circle on the surface of a sphere whose center is the center of the sphere.
- greatest common divisor/factor. The greatest common divisor of a sequence of integers, is the largest integer that divides each of them exactly.
- hexagon . A plane figure having six sides and six angles.
- hyperbola. A plane curve generated by a point so moving that the difference of the distances from two fixed points is a constant: a curve formed by the intersection of a double right circular cone with a plane that cuts both halves of the cone. A curve with equation x2/a2-y2/b2=1. or 2+y2/b2-z2/c2=-1.
- hypotenuse. The longest side of a right triangle.
- icosaedron . A polyhedron having 20 faces.
- identities.. Algebraic relationships:
- (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
- (a + b)(a - b ) = (a2 - b2)
- a(b + c) = ab + ac
- 1/a - 1/b = (b -a)/(ab)
- imaginary number. A complex number of the form xi where x is real and i=sqrt(-1).
- imaginary part. The imaginary part of a complex number x+iy where x and y are real is y.
- index. A superscript indicating the number of times a number is multiplied by itself. Examples of indexes are:
- an x am = a(n +m)
- a-n = 1/an
- a1/n = nÖa
- (an)m = anm
- inequality. The statement that one quantity is less than (or greater than) another.
- infinitesimal. A variable that approaches 0 as a limit.
- inflection. A point of inflection of a plane curve is a point where the curve has a stationary tangent, at which the tangent is changing from rotating in one direction to rotating in the oppostie direction.
- integer. One of the numbers ..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ... A whole number.
- irrational number. Any real number that is not rational, that is it cannot be written as a terminating or repeating decimal. These include p, e and Ö2.
- isosceles tetrahedron. A tetrahedron in which each pair of opposite sides have the same length.
- isosceles triangle. A triangle with two equal sides.
- isosceles trapezoid. Ain which the two non-parallel sides have the same length.
- least common multiple. The least common multiple of a set of integers is the smallest integer that is an exact multiple of every number in the set.
- linear function. A function of the form y=ax+b.
- line segment. The part of a line between two given distinct points on that line (including the two points).
- logarithm. A logarithm is the exponent of a number to a specified base. If bn = x then n is the logarithm of x to the base b.
- lowest common denominator. The smallest number that is exactly divisible by each denominator of a set of fractions.
- major axis. The major axis of an ellipse is it's longest chord.
- maximum. The largest of a set of values.
- mensuration. The act of measuring. Geometry applied to the computation of lengths, areas, or volumes from given dimensions or angles.
- minor axis. The minor axis of an ellipse is its smallest chord.
- minimum. The smallest of a set of values.
- mode. The most frequently occurring value in a sequence of numbers.
- multiple. The integer b is a multiple of the integer a if there is an integer d such that b=da.
- natural number. Any one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... .
- negative number. A number smaller than 0.
- normal. perpendicular
- numbers. Numbers are either real or complex. Real numbers are those used for counting and range from - to + . Complex numbers are those that contain Ö-1 , usually denoted i so that i2 = -1.
- number line. A line on which each point represents a real number.
- numerator. In the fraction x/y, x is called the numerator and y is called the denominator.
- oblique angle. an angle that is not 90o
- oblique triangle. A triangle that is not a right triangle.
- obtuse angle. an angle larger than 90o but smaller than 180o
- obtuse triangle. A triangle that contains an obtuse angle.
- octagon . A plane figure having eight angles and eight sides.
- octoedron . A solid bounded by eight plane faces.
- odd number. An integer that is not divisible by 2.
- ordinate. The y-coordinate of a point in the plane.
- origin. The point in a coordinate plane with coordinates (0,0).
- parabola . A plane curve generated by a point moving so that its distance from a fixed point is equal to its distance from a fixed line: the intersection of a right circular cone with a plane parallel to an element of the cone.
- parallel . Lying or extending alongside of one another and always at the same distance apart; continuously equidistant: said of two or more lines, surfaces, or concrete things.
- parallelogram . A four-sided rectilineal figure whose opposite sides are parallel but the internal angles are greater or less than 90 degrees.
- percentage. A number represented as a fraction of 100. Percentages may be written as a proper fraction or as a decimal fraction, ie: 48% is 48/100 or 0.48.
- perfect number. A positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors. For example, 28 is perfect because 28=1+2+4+7+14.
- perpendicular . Situated at right angles to the plane of the horizon, or directly up or down; vertical.
- prime. A prime number is an integer larger than 1 whose only positive divisors are 1 and itself.
- Pythagorean triangle. A right triangle whose sides are integers.
- platonic solids (polyhedrons). Solids with faces of equal shape. There are only five:
- Tetrahedron - 4 triangular faces
- Cube - 6 square faces
- Octahedrons - 8 triangular faces
- Dodecahedron - 12 pentagonal faces
- Icosahedron - 20 triangular faces
- polygons. Figures with sides of equal length and equal internal angles. The first 10 are:
- Triangle - 3 sides
- Quadrangle - 4 sides
- Pentagon - 5 sides
- Hexagon - 6 sides
- Heptagon - 7 sides
- Octagon - 8 sides
- Nonagon - 9 sides
- Decagon -10 sides
- Dodecagon - 12 sides
- Icosagon - 20 sides
- power. A general term for squares, cubes etcetera.
- primes. Numbers whose only factors are 1 and itself. Unity (1) is not a prime. The first seven primes are: 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17 and 19.
- probability. The likelyhood that something will happen.
- Pythagoras' Theorem. For any right-angled triangle, the square of the longest side (R) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (x and y)
- QED. Abbreviation for quod erat demonstrandum, used to denote the end of a proof.
- quadrangular prism. A prism whose base is a quadrilateral.
- quadrangular pyramid. A pyramid whose base is a quadrilateral.
- quadrant. Any one of the four portions of the plane into which the plane is divided by the coordinate axes.
- quadratic equation. An equation of the form f(x)=0 where f(x) is a second degree polynomial. That is, ax2 + bx + c = 0.
- quadrilateral. A geometric figure with four sides.
- quotient. The result of a division.
- radians. Circular measure where the circumference of a circle is divided in to a number of arcs each equal in length to the radius. There are 2pi radians in 1 revolution. One radian = 180/pi degrees. One radian is approximately 57.3o.
- ratio. quotient of two numbers.
- rational number. A rational number is a number that is the ratio of two integers. All other real numbers are said to be irrational. All rational numbers can be written as a terminating or repeating decimal.
- real part. The real number x is called ther eal part of the complex number x+iy where x and y are real and i=sqrt(-1).
- reciprocal. A number divided into 1. The reciprocal of 7 is 1/7.
- reflex angle. An angle between 180o and 360o.
- rhombus. A parallelogram with four equal sides.
- right angle. an angle formed by two perpendicular lines; a 90o angle.
- right triangle. A triangle that contains a right angle.
- scalene triangle. A triangle with unequal sides.
- secant. A straight line that meets a curve in two or more points.
- sequence. A collection of numbers in a prescribed order: a1, a2, a3, a4, ...
- series. The sum of a finite or infinite sequence
- similar figures. Two geometric figures are similar if their sides are in proportion and all their angles are the same.
- spherical trigonometry. The branch of mathematics dealing with measurements on the sphere.
- square. A quadrilateral with 4 equal sides and 4 right angles.
- square number. A number of the form n^2.
- supplementary. Two angels are supplementary of they add up to 180o.
- tangent. A line that meets a smooth curve at a single point and does not cut across the curve.
- torus. A geometric solid in the shape of a donut.
- transcendental number. A number that is not algebraic.
- trapezium. A quadrilateral in which no sides are parallel.
- trapezoid. A quadrilateral in which two sides are parallel.
- triangle. A geometric figure with three sides. The sum of the internal angles of any triangle is 180 . The four basic triangle types are:
- right-angled - one angle equal to 90o
- isosceles - two sides of equal length
- equilateral -all sides of equal length
- scalene -no equality in any of the sides.
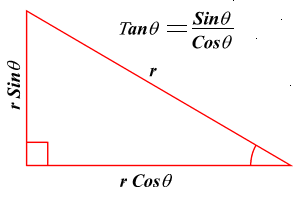
- trigonometry. The branch of mathematics exploiting the properties of right angled triangles. The trigonometric identities are: sine, cosine and tangent and are determined as follows:
- truncated pyramid. A section of a pyramid between its base and a plane parallel to the base.
- twin primes. Two prime numbers that differ by 2. For example, 11 and 13 are twin primes.
- unilateral surface. A surface with only one side, such as a Moebius strip.
- unit circle. A unit circle is a circle with radius 1.
- unit cube. A cube with edge length 1.
- unit fraction. A fraction whose numerator is 1.
- unit square. A unit square is a square of side length 1.
- unity. one
- volume. The measure of spce occupied by a solid body.
- vulgar fraction. A common fraction.
- whole number. A natural number.
- x-axis. The horizontal axis in the plane.
- x-intercept. The point at which a line crosses the x-axis.
- y-axis. The vertical axis in the plane.
- y-intercept. The point at which a line crosses the y-axis.
Saturday, January 1, 2011
SOME MATHEMATICAL TERMS:
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

RTPS The RTPS Centre at Bihar Bhawan was officially opened by the Hon’ble Chief Minister Bihar on 15 Aug 2012 to be a place to collect the Caste, Income, and Residential Certificates.
ReplyDeletefactorial hundred In the last few days, the “factorial of 100” is one of the top subjects and a lot of maths geeks compute it using voice assistants such as Alexa, Shiri, etc.
In the last few days, the “factorial of 100” is one of the top subjects and a lot of maths geeks compute it using voice assistants such as Alexa, Shiri, etc.
cciv-stock Stocks rose on Friday after news of Churchill Capital’s (NYSE:CCIV) Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC) closing its merger with Lucid Motors.